Network Interface Card For Mac
Definition of MAC Address in Network Encyclopedia. What is MAC Address? MAC Address is a unique 6-byte (48-bit) address that is usually permanently burned into a network interface card or other physical-layer networking device and that uniquely identifies the device on an Ethernet-based network.A MAC address is also known as an Ethernet address, hardware address, physical address, or PHY address. Network Interface Controller (NIC) or Network Card is a device that enables communication between devices of a particular computer network.Computers can be connected either with a cable or using wireless. How does it work? The network card provides connection between the Computer and the outside world. Every device (e.g. Desktop, notebook, tablet, phone, or TV that communicates over a.
Definition of MAC Address in Network Encyclopedia.
What is MAC Address?
MAC Address is a unique 6-byte (48-bit) address that is usually permanently burned into a network interface card (NIC) or other physical-layer networking device and that uniquely identifies the device on an Ethernet-based network.
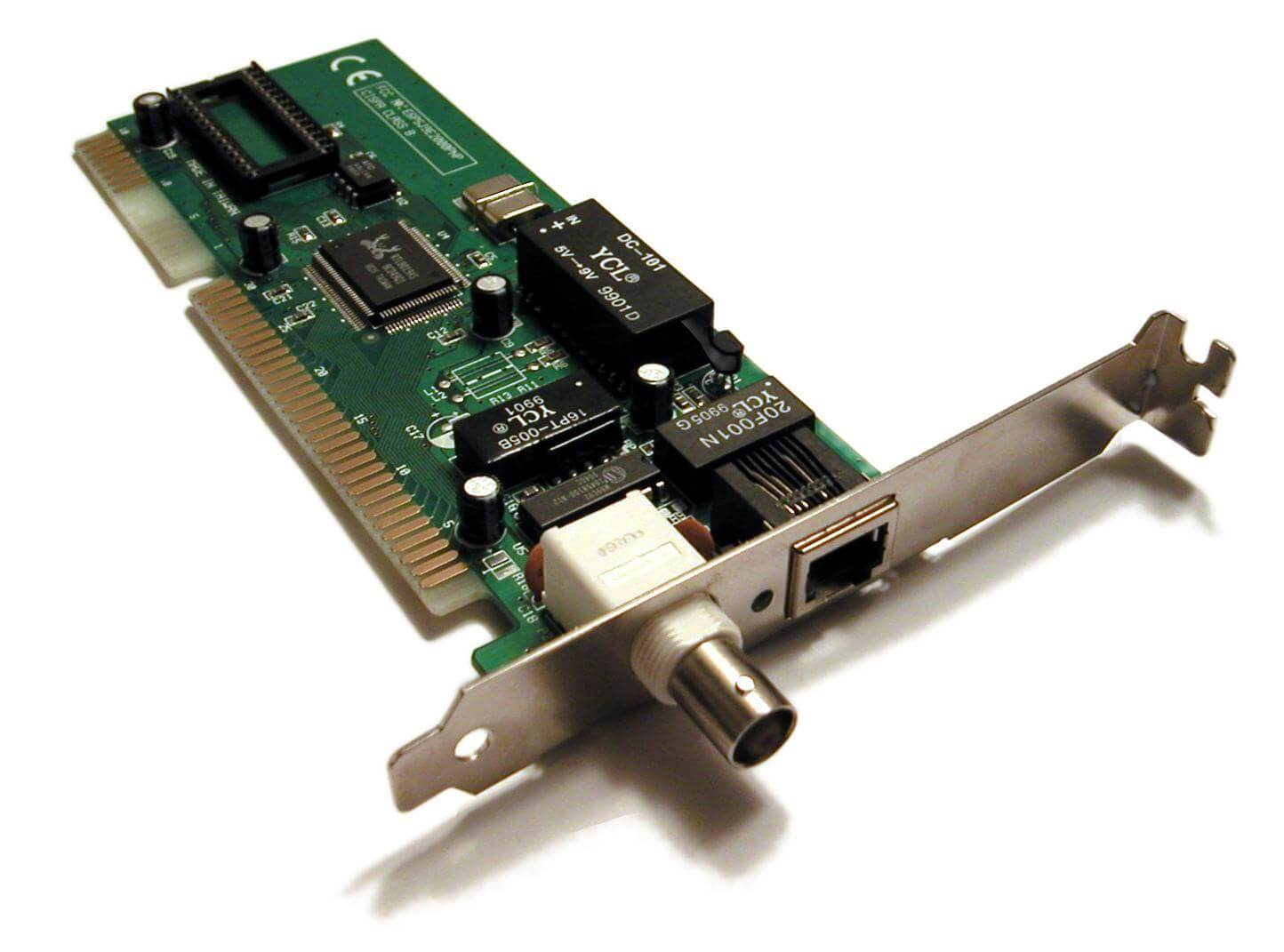
A MAC address is also known as an Ethernet address, hardware address, physical address, or PHY address.
How MAC address Works
MAC addresses can be hard-coded into circuitry or stored in read-only memory (ROM), and they can be configured using vendor-supplied software. The uniqueness of MAC addresses is ensured by the Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers (IEEE), which assigns networking device vendors specific blocks of MAC addresses for the devices they produce. The first 3 bytes (24 bits) represent the manufacturer of the card, and the last 3 bytes (24 bits) identify the particular card from that manufacturer. Each group of 3 bytes can be represented by 6 hexadecimal digits, forming a 12-digit hexadecimal number representing the entire MAC address. Examples of manufacturer 6-digit numbers include the following:
- 00000C (Cisco)
- 00001D (Cabletron)
- 0004AC (IBM [PCMCIA Ethernet adapter])
- 0020AF (3Com)
- 00C0A8 (GVC)
- 080007 (Apple)
- 080009 (Hewlett-Packard)
Each frame on an IP-based local area network (LAN) contains a source MAC address and destination MAC address in its header. These addresses are added to the frame by the media access control (MAC) layer of the protocol stack.
Every device and port that connects to an Ethernet LAN requires a MAC address. These MAC addresses are used by devices such as bridges and Layer 2 switches for building routing tables to direct traffic through the network. Bridges gather MAC addresses by examining the source MAC address of every frame of network traffic they receive.
They then use these source addresses for building their internal routing tables, which they use to forward frames only to the segment that has the station with that particular destination MAC address. This process reduces network congestion by avoiding the need for bridges to forward broadcasts.
Changing MAC Address
Some NICs come with a software utility that you can use to change the MAC address of the card. Changing the address is not a good idea! If you accidentally configure two network cards on your network to have the same MAC address, address conflict problems will result and the computers will not be able to communicate on the network. However, some NICs, such as Token Ring cards, actually require you to assign a unique MAC address to them before they will work.
What Is Network Interface Card
How to find MAC Address
To determine the MAC address of your computer’s NIC, use the following commands:
Network Interface Card For Mac Os
- From the latest Microsoft Windows OS command prompt: ipconfig /all
- From the Windows 95 or Windows 98 Run dialog box: winipcfg
